Introduction
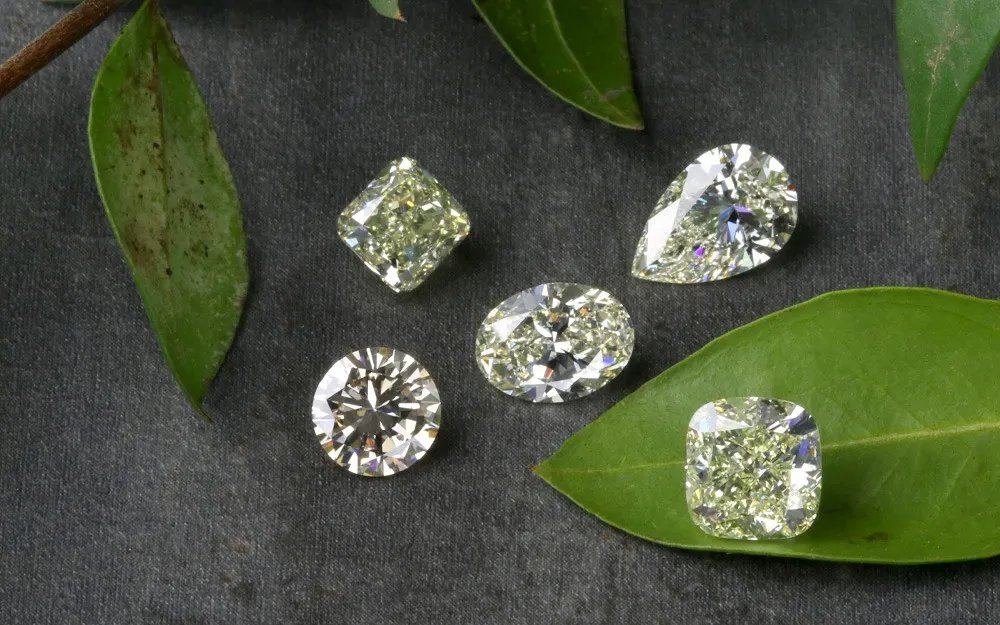
Diamonds are among the most coveted gemstones globally, prized for their beauty, rarity, and enduring symbolism. When it comes to assessing the quality and value of a diamond, experts and buyers alike turn to the 4Cs: Carat Weight, Cut, Clarity, and Color. Understanding these fundamental characteristics is crucial for making informed decisions when purchasing or investing in diamonds.
Understanding the 4Cs
Carat Weight
The carat weight of a diamond refers to its size and is one of the most apparent factors influencing its value. Contrary to popular belief, what matters in the diamonds 4cs, carat weight doesn’t solely determine a diamond’s worth. While larger diamonds often command higher prices, other factors such as cut quality, clarity, and color also play significant roles in determining a diamond’s overall appeal and value.
Cut Quality
The cut of a diamond is perhaps the most crucial factor affecting its brilliance and sparkle. A well-cut diamond reflects light internally, creating a mesmerizing play of light and maximizing its beauty. Conversely, a poorly cut diamond may appear dull and lackluster, diminishing its overall allure. Different cut grades, ranging from Excellent to Poor, indicate the quality of a diamond’s cut, with Excellent cuts exhibiting superior brilliance and fire.
Clarity Grade
The clarity grade of a diamond assesses the presence of internal flaws (inclusions) and surface blemishes (blemishes). Diamonds with fewer inclusions and blemishes are considered higher in clarity and are generally more valuable due to their rarity and perceived purity. However, it’s essential to note that most diamonds have some degree of imperfections, and minor flaws may not detract significantly from a diamond’s beauty, especially when they’re not visible to the naked eye.
Color Grade
Diamond color grading evaluates the presence of color in a diamond, ranging from colorless to yellow or brown hues. Colorless diamonds are highly prized for their purity and brilliance, while diamonds with noticeable color may be graded lower on the color scale. However, colored diamonds, such as fancy yellow or pink diamonds, are exceptions to this rule and are valued for their unique hues.
Interplay of the 4Cs
The 4Cs of diamonds are interconnected, with each factor influencing the others. For example, a well-cut diamond can enhance its apparent size and minimize the visibility of inclusions, improving its clarity. Likewise, a diamond with higher clarity and color grades may appear more brilliant when expertly cut, maximizing its overall beauty and value.
Selecting the Perfect Diamond
Choosing the perfect diamond involves striking a balance between the 4Cs to meet individual preferences and budget considerations. While some may prioritize carat weight for a larger stone, lab diamonds, others may value cut quality or clarity for superior brilliance and purity. Understanding personal preferences and educating oneself about the 4Cs are essential steps in selecting a diamond that best suits one’s needs and desires.
Tips for Diamond Buyers
When purchasing a diamond, buyers should consider several key factors to ensure they’re making a wise investment. It’s advisable to shop with reputable jewelers who offer certified diamonds and provide detailed information about the 4Cs of each stone. Additionally, asking questions and seeking guidance from experienced professionals can help buyers make informed decisions and find the perfect diamond within their budget.
Investing in Diamonds
Beyond their aesthetic appeal, diamonds can also serve as valuable investments. While the diamond market may fluctuate, high-quality diamonds with desirable characteristics tend to retain their value over time. Factors such as rarity, demand, and market trends can influence the investment potential of diamonds, making them an attractive option for diversifying investment portfolios.
Emerging Trends in Diamond Grading
Advancements in technology have revolutionized the diamond grading process, allowing for more accurate and consistent evaluations of the 4Cs. Innovations such as automated grading systems and artificial intelligence algorithms are reshaping the diamond industry, providing buyers with greater transparency and confidence in their diamond purchases.
Diamond Certification
For assurance of quality and authenticity, it’s advisable to purchase certified diamonds from reputable sources. Diamond certification involves rigorous testing and evaluation by independent gemological laboratories, such as the Gemological Institute of America (GIA) or the International Gemological Institute (IGI). Certified diamonds come with detailed grading reports that provide information about the 4Cs, enabling buyers to make informed decisions with confidence.
Ethical and Sustainable Diamonds
In recent years, there has been a growing demand for ethically sourced and sustainably produced diamonds. Consumers are increasingly conscious of the social and environmental impact of their purchases and are seeking reassurance that the diamonds they buy are ethically sourced and mined. Initiatives such as the Kimberley Process Certification Scheme and the Responsible Jewellery Council aim to promote ethical practices and sustainability in the diamond industry, ensuring that diamonds are mined and processed responsibly.
Common Misconceptions about the 4Cs
Despite their importance, there are several common misconceptions surrounding the 4Cs of diamonds. For example, many believe that carat weight is the sole determinant of a diamond’s value, overlooking the significance of cut, clarity, and color. Additionally, some may assume that higher clarity or color grades guarantee a more beautiful diamond, disregarding the importance of cut quality in maximizing a diamond’s brilliance and fire. By debunking these myths and clarifying misunderstandings, buyers can make more informed decisions when purchasing diamonds.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the 4Cs—Carat Weight, Cut, Clarity, and Color—are essential factors to consider when evaluating the quality and value of a diamond. Each C plays a significant role in determining a diamond’s beauty, brilliance, and overall appeal. By understanding the interplay of these factors and considering personal preferences and budget