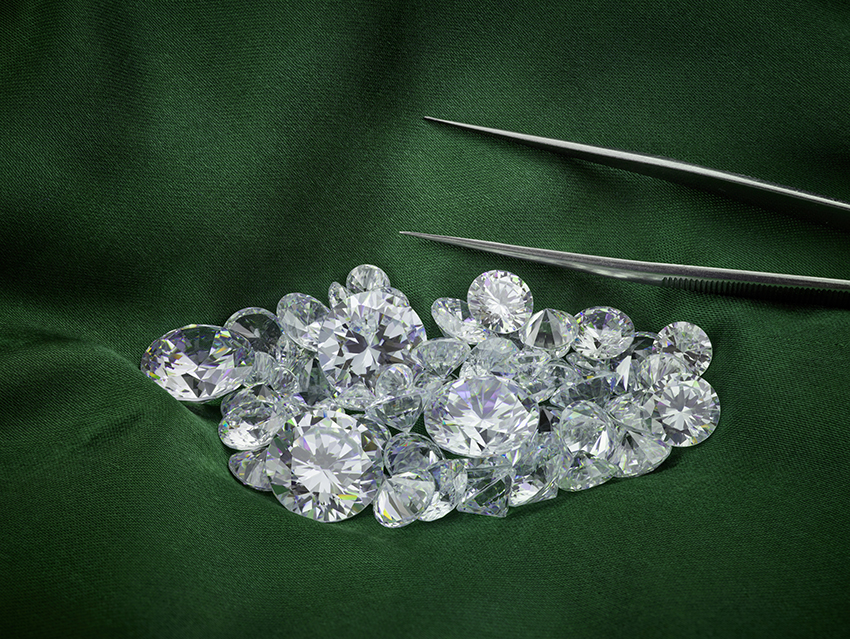
In recent years, lab diamond tennis necklaces have emerged as a trendy and sustainable choice for jewelry enthusiasts. These exquisite pieces, adorned with lab-created diamonds, offer the same brilliance and elegance as their mined counterparts while coming with a host of benefits that appeal to a modern, conscious consumer base. This article explores the allure of lab diamond tennis necklaces, the process behind lab-created diamonds, and why they are becoming a preferred option for many.
What Are Lab Diamond Tennis Necklaces?
A tennis necklace is characterized by a continuous line of diamonds, typically set in precious metals like gold or platinum. Its name is believed to originate from professional tennis player Chris Evert, who famously wore a diamond necklace during a match in the 1980s, leading to the style’s popularity.
Lab diamond tennis necklaces are crafted using lab-created diamonds, which are chemically and physically identical to natural diamonds. These necklaces can range in design from classic styles with round brilliant cut diamonds to more contemporary variations incorporating different shapes and settings.
The Process of Creating Lab-Created Diamonds
Lab-created diamonds are formed through two primary methods: High Pressure High Temperature (HPHT) and Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD).
High Pressure High Temperature (HPHT) is a method that mimics the natural diamond formation process by recreating the extreme pressure and temperature conditions found deep within the Earth. Carbon is subjected to these conditions, resulting in the formation of diamonds.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) involves introducing a carbon-containing gas into a chamber, where it is ionized to create a plasma. This plasma then deposits carbon onto a substrate, gradually forming a diamond.
Both methods produce diamonds that are visually and chemically identical to natural diamonds, leading to the same brilliance, durability, and fire.
Benefits of Lab-Created Diamonds
One of the most significant advantages of lab-created diamonds is their ethical sourcing. Unlike mined diamonds, which can be associated with conflict and environmental concerns, lab-created diamonds are produced in controlled environments, ensuring they are free from ethical dilemmas.
In addition to their ethical implications, lab-created diamonds are typically 20-40% less expensive than their mined counterparts. This cost-effectiveness allows consumers to invest in larger or higher-quality stones without breaking the bank, making lab diamond tennis necklaces an appealing choice.
Furthermore, the production of lab-created diamonds requires fewer natural resources and has a smaller environmental footprint compared to traditional diamond mining. By choosing lab diamond jewelry, consumers can feel confident that they are making a sustainable choice.
Lab-created diamonds also come in a wide range of shapes, sizes, and qualities, allowing for personalized designs that cater to individual tastes. This variety ensures that buyers can find the perfect tennis necklace to match their style.
The Timeless Appeal of Tennis Necklaces
Tennis necklaces are a timeless piece of jewelry that can elevate any outfit, from casual wear to formal attire. Their versatile nature makes them suitable for various occasions, including weddings, anniversaries, and everyday wear. The sparkling allure of lab-created diamonds only enhances their appeal, as wearers can enjoy the luxurious look of diamonds without the associated ethical concerns.
Conclusion
Lab diamond tennis necklaces represent a harmonious blend of elegance, ethical sourcing, and affordability. As consumers become more conscious of the environmental and social implications of their purchases, lab created diamonds are stepping into the spotlight as a responsible and stylish choice. Whether for a special occasion or a treat for oneself, these necklaces offer a dazzling way to embrace both beauty and sustainability.